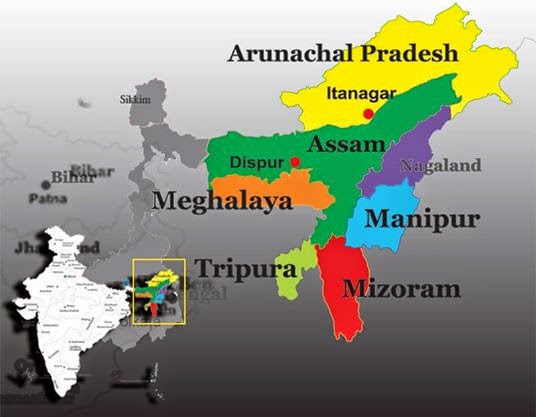
Often referred to as the “Gateway to North-East India”, Assam is one among the eight North-East sisters. Known as the land of rivers, mystic valleys and blue hills, it is one of the most important states of the region surrounded by rainforest, mighty rivers, exalted hills, plains, rare species of flora and fauna as well as river islands. Situated at 8905’-960 1’ East Longitude and 2403’-27058’ North Latitude, Assam covers a total area of 78,433sq km.
 |
| Indian State of Assam |
Until India attained independence in the year 1947 from the British Rule, Assam included most of the North-eastern state except for Manipur on the east and Tripura on the south. The present day Assam is just a small part of the erstwhile state, which has been divided into Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh in the year 1970. The state shares International boundaries with Bhutan in North and Bangladesh in South-West. Assam along with its 6 sisters is linked with other parts of India through a constricted stripe of land in West Bengal known as the Siliguri Corridor. Assam is one of the most enchanting and mesmerizing states of India, endowed with natural bounties. Geographically, the state is segregated into three regions, namely the Brahamaputra River Valley, the Barak Valley and the hilly provinces of North Cachar Hills and the Karbi Anglong, which divides the both the regions.
The northern part of Assam is completely occupied by the extended valley formed by the river Brahmaputra, which is the lifeline of the state. This valley is most densely populated region of the state, which is enclosed by the foothills of the Himalayas on the north and hills on the south and is the principal physical aspect of the enchanting state. As the mighty river Brahmaputra enters the state near Sadiya situated in the northeast corner and runs westward for nearly 450 miles before turning south to enter the plains of Bangladesh. This river valley is speckled with hills and valleys.
In the middle of Assam, towards the south of the hills is the Barak Valley division which is also known as Surama Valley shares its borders with Bangladesh. It is enclosed by Manipur, North Cachar and Mizoram. This valley is dominated by the Barak River, which flows in the course of the valley and finally meets with the Brahmaputra River in Bangladesh. This is the most fertile valley as it experiences a lot of flood and is characterized by lakes and hills. Both the valleys are demarcated by the hilly region of North Cachar Hills and Karbi Anglong.
Assam is rich in natural resources and is a well-known producer of crude oil. Natural Gas, magnetic quartzite, feldspar, clay, sillimanites, limestone, coal, kaolin and a little amount of iron ore are some of the natural resources found in the state. It is also a home of several engendered animals and houses a number of forest reserves and national park, which are home to a variety of wild animals and avian species.
The state of Assam features Tropical Monsoon Rainforest Climate and experiences humidity and heavy rainfall. The state experiences a maximum temperature of 35–38 °C during summer and 6–8 °C during winter. Normally the monsoon season starts from June, however, some rainfall is also experienced during the month of April.




thank u blogger
ReplyDelete